2 – Customer Segments
Discover how to identify and define customer segments to enhance your business model and effectively meet your audience's unique needs.

A look at the business model from the product manager's point of view
CANVAS 13 - Great guide on the business model, from the product manager's point of view
1 – Customer Problem
You are here ➔ 2 – Customer Segments
3 – Value Propositions
Value Proposition Formulation Map
4 – Customer Relationships
5 – Channels
6 – Revenue Streams
7 – Key Activities
8 – Key Resources
9 – Key Partners
10 – Cost Structure
11 – Eco-Social Costs
12 – Eco-Social Benefits
13 – KPI (Key Performance Indicators)
What are Customer Segments?
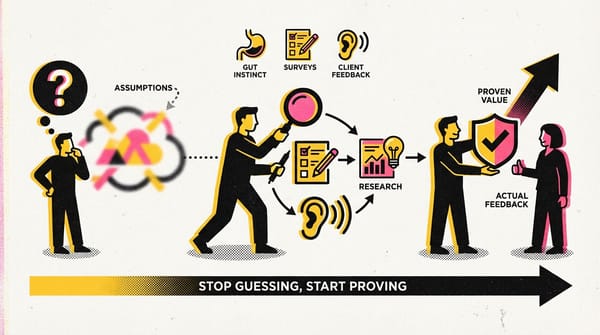
Customer segments are a key element of the Canvas business model and an important task for product managers. In the context of our work, we consider them through the Customer Development (CustDev) tool.
Customer segments are groups of people or organizations that a business recognizes as its target audience. They turn to your product or service to solve their unique problems. They are defined based on common characteristics, needs, and behaviors, and each of them may have different needs that your product or service must meet. Understanding your customer segments allows the business to better meet their needs and offer more valuable products and services.
In this article, I will explain what customer segments are, how to identify them, and what types of segments exist in the context of the Canvas business model. I will also mention the main participants in the purchasing process to build effective market communication.
The Importance of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation plays a key role in business success for several reasons:
- Personalization of offer: By understanding the features of each segment, a business can offer more suitable products and services.
- Efficient use of resources: Marketing and sales efforts can be focused on the most promising segments, which increases efficiency.
- Improving customer relationships: A business can build stronger and longer-lasting relationships with customers by offering them what they really need.
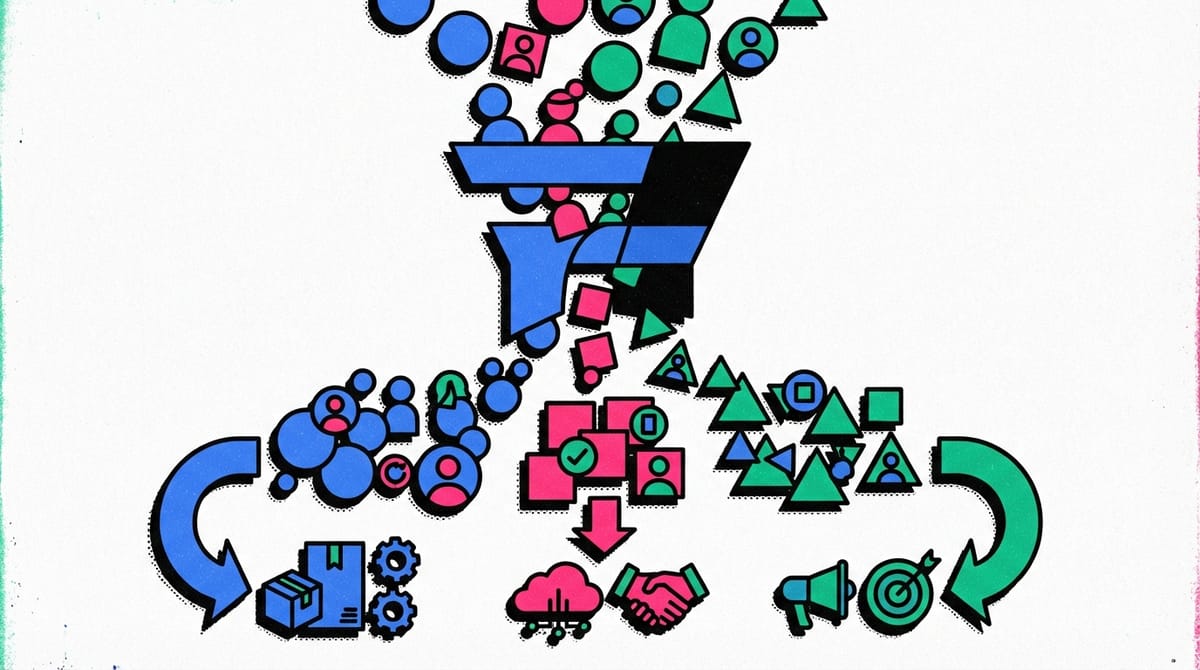
Types of Customer Segments
In the context of the Canvas business model, several types of customer segments can be distinguished:
- Mass market: Oriented towards a wide range of consumers with similar needs and problems. Examples include electronics manufacturers or retail chains.
- Niche market: Oriented towards a narrow circle of consumers with very specific needs. An example would be suppliers of specialized medical equipment.
- Segmented market: Includes several small segments with different needs and problems but related to each other. For example, a bank may offer various types of credit products for students, retirees, and young families.
- Diversified market: Oriented towards several unrelated customer segments. A classic example is Amazon, offering both cloud services for businesses and retail goods for end consumers.
- Multi-sided market (multi-sided platforms): Includes two or more interdependent segments. An example is the Uber platform, connecting drivers and passengers.
Main Participants in the Purchase Process
An important aspect of developing a sales strategy is understanding the main participants in the purchase process. These participants play a key role in the turnover of your product in the market.