3 – Value Propositions
Unlock the secrets of value propositions! Discover how to craft compelling offerings that resonate with customers and drive success.

A look at the business model from the product manager's point of view
CANVAS 13 - Great guide on the business model, from the product manager's point of view
1 – Customer Problem
2 – Customer Segments
You are here ➔ 3 – Value Propositions
Value Proposition Formulation Map
4 – Customer Relationships
5 – Channels
6 – Revenue Streams
7 – Key Activities
8 – Key Resources
9 – Key Partners
10 – Cost Structure
11 – Eco-Social Costs
12 – Eco-Social Benefits
13 – KPI (Key Performance Indicators)
2 – Value Proposition
I already have an article on this topic. It is short and contains a simple but complete formula for formulating a value proposition.
The value proposition is what makes a product or service attractive to buyers. It can be a unique feature that distinguishes the product from competitors, or a solution to a problem that customers face.
For example, services can offer a high level of commitment and individual focus, paying attention to the business and the customer's needs.
This can be a resource, an information site, a virtual assistant, or an application to increase productivity. It can be accessible, structured, regularly updated, and include a step-by-step plan for individual work. This resource or tool should be convenient, functional, and have community support, and all this, for example, for a small monthly fee. It's like a Swiss Army knife: a tool capable of performing many tasks.
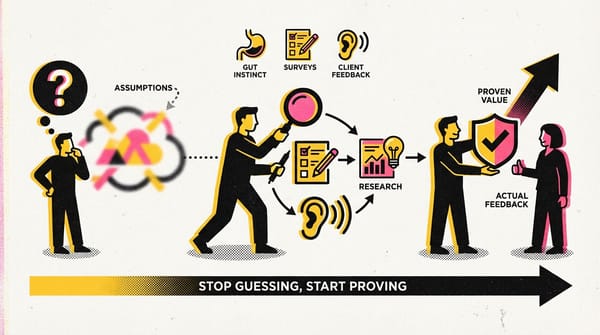
Examples of factors that influence customer decision-making
Functional Aspects