5 – Channels
Discover the essential channels for delivering value to your customers. Learn how to enhance relationships and boost your business model effectively!
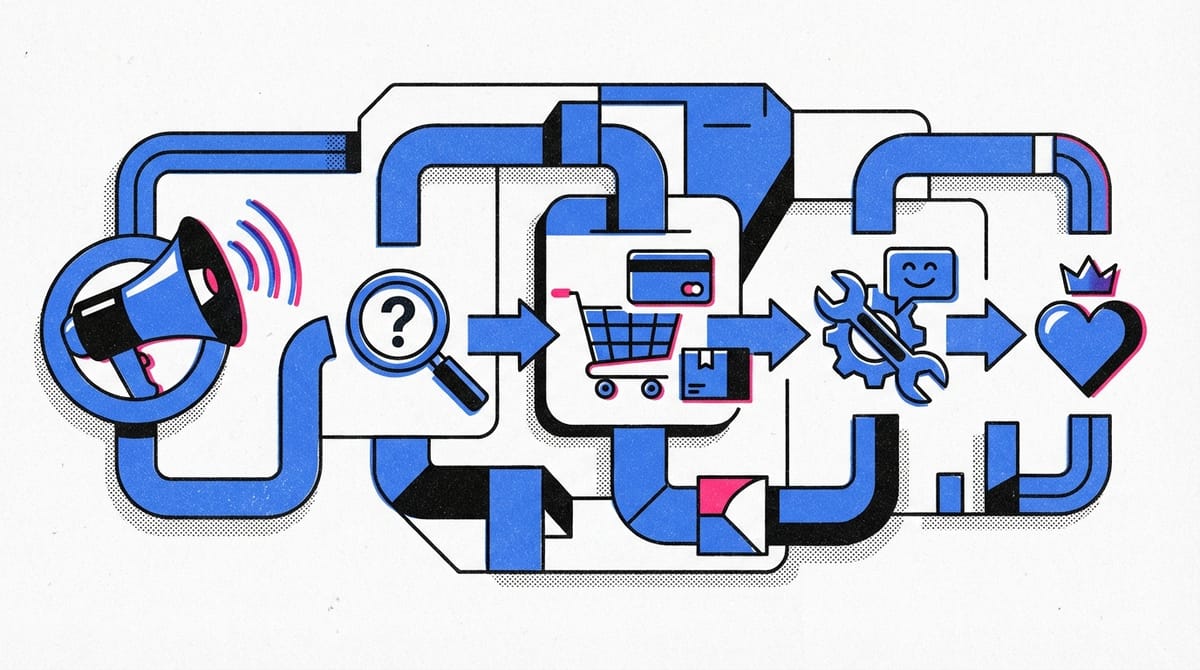
A look at the business model from the product manager's point of view
CANVAS 13 - Great guide on the business model, from the product manager's point of view
1 – Customer Problem
2 – Customer Segments
3 – Value Propositions
Value Proposition Formulation Map
4 – Customer Relationships
You are here ➔ 5 – Channels
6 – Revenue Streams
7 – Key Activities
8 – Key Resources
9 – Key Partners
10 – Cost Structure
11 – Eco-Social Costs
12 – Eco-Social Benefits
13 – KPI (Key Performance Indicators)