Building a Business with Minimal Costs Using MVP
Learn how to build a business with minimal costs using MVP. Discover strategies to test ideas, save resources, and validate your market.
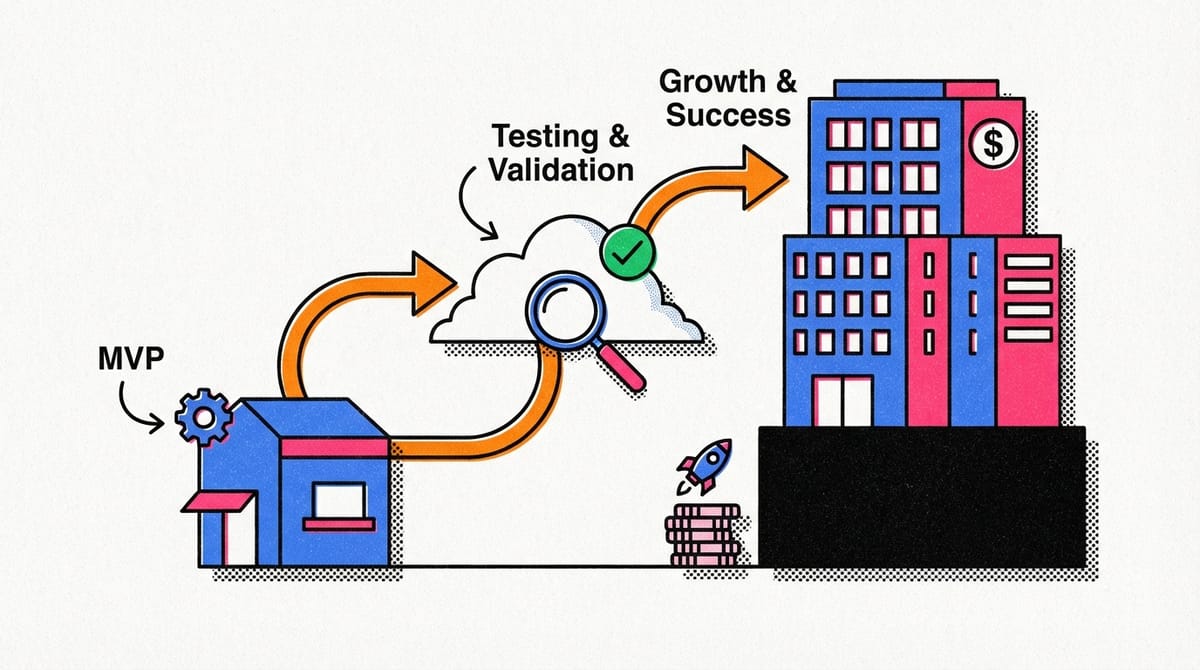
MVP is the process of verifying a value hypothesis with minimal time and effort.
MVP is a product with a minimal but sufficient set of features.
What types of MVPs exist?
- MVP to verify the product's value.
- MVP to verify the value of a feature.
- MVP to obtain data.
What is the purpose of MVP?
- Reduce the risk of uncertainty.
- Save time and money.
- Reduce the risk of focusing incorrectly by minimizing the chance of confusing what we want with reality.
- Understand metrics (LTV, CAC, sales funnel, etc.)
When is it time to make an MVP?
Approach 1: MVP as a process
Approximate duration: 10 days.
- Market research - finding problems in the market.
- Formulation of a problem hypothesis.
- Confirmation of the problem - communication with potential customers.
- Value proposition - the solution we offer to the customer.
- Model the economics.
- Confirmation of the solution: determining if there are sales or not. If there are no sales, you can go back to the previous step, reformulate the hypothesis, or conduct a survey with another sample of the audience and relaunch.
Approach 2: Express test of MVP
Approximate duration: 3-4 days.
- Market research - finding problems in the market.
- Formulation of a problem hypothesis.
- Confirmation of the problem - without communication with customers.
- Confirmation of the problem - in case of the first sales, you can talk to the users, find out what they bought, and what problems they solved.
Types of MVP
- Prototypes (electronic and paper).
- Landing page (description of the service and features). With a landing page, you can create the impression that the product already exists.
- Presale (mainly crowdfunding) - a platform where information about the product is placed, and users can make presales, obtaining discounts, bonuses, and other advantages.
- Manual work.
- Groups on social networks and messaging.
- Decisive interviews for B2B product - presentations and prototypes.
Examples of MVP
Zappos
Zappos launched in 1999 as an online shoe store, which was not very common at the time. The founder decided to sell shoes online: he went to the nearest shoe store, took pictures of the shoes, and posted them on the website. When people placed orders, he mailed the shoes. This way, he verified his hypothesis that people were willing to buy shoes online.
Book: "Delivering Happiness" by Zappos.
Dropbox
In 2007, the hypothesis arose: what if people store files in the cloud instead of locally? Buying servers, cooling systems, etc., was costly. Instead, a video was created demonstrating the product's operation, functionality, and the needs it satisfies. In a few days, tens of thousands of people responded to the video.
Replacement of a damaged bumper
Find an unpainted bumper online, determine the most popular car brand, find all the car colors of that brand, and create a landing page with traffic (through contextual advertising) to attract customers. If there is demand, you can invest in the product's implementation.
Within the framework of MVP, it is not necessary to have a finished product. Dream and test.