The role of simple statistics in data science
Discover how simple statistics empower data science, enabling better decision-making and insights. Enhance your skills and understanding today!
- Statistics is foundational to data science: It enables the collection, analysis, and interpretation of ever-growing amounts of data.
- Everyday applications: Statistical concepts are used in daily life through weather forecasts, sports statistics, polls, and medical data.
- Professional applications: Data professionals use statistics to:
- Identify patterns in data
- Analyze uncertainty
- Generate insights
- Make predictions
- Solve complex problems
- Common statistical concepts: Understanding fundamentals like probability, averages, margin of error, percentiles, and medians is essential.
- Foundation for advanced analysis: Basic statistics knowledge leads to more complex methods like hypothesis testing, classification, regression, and time series analysis.
- Common language: Statistics provides a shared vocabulary for data professionals, similar to how grammar enables language communication.
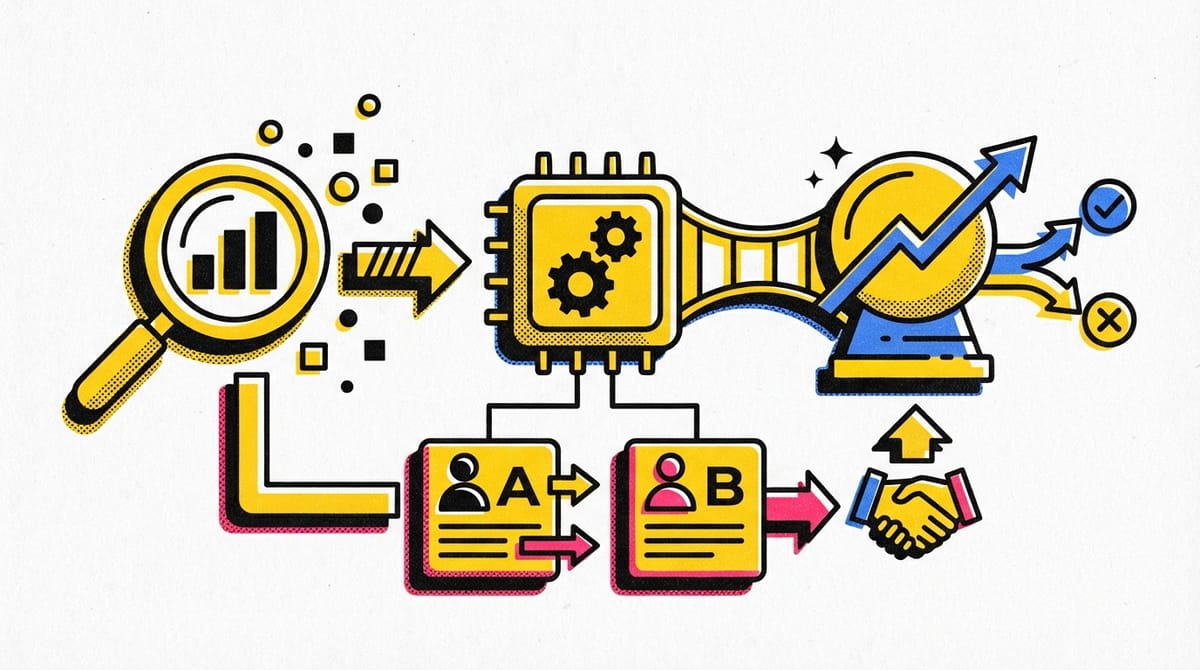
Statistics in action: A/B testing
- A/B Testing Definition: A method to compare two versions of something (like webpages, emails, or ads) to determine which performs better
- Business Applications: Companies use A/B testing to optimize website design, marketing emails, online ads, and improve customer experience
- Statistical Concepts Used:
- Sampling - selecting a subset of data from a population
- Inferential statistics - making predictions about populations based on samples
- Confidence intervals - ranges that describe uncertainty in estimates
- Statistical significance - determining if results are due to chance or real differences
- Decision Making: A/B testing provides data-driven evidence for making changes to improve business outcomes
- Sample Size Importance: Choosing the right sample size is crucial for obtaining valid test results and avoiding statistical errors
- Practical Value: Even small changes (like button size) can lead to significant improvements in conversion rates and financial gains.
Descriptive statistics versus inferential statistics
- Descriptive Statistics:
- Summarize and describe main features of a dataset
- Include visuals (graphs, tables) and summary statistics
- Help understand large amounts of data quickly
- Use measures of central tendency (mean) and dispersion (standard deviation)
- Inferential Statistics:
- Allow making inferences about populations based on samples
- Used to draw conclusions and make predictions
- Require representative samples to be reliable
- Involve parameters (population characteristics) and statistics (sample characteristics)
- Population vs Sample:
- Population includes all possible elements of interest
- Sample is a smaller subset of the population
- Samples must be representative to draw valid conclusions
- Used when studying entire populations is impractical
- Parameters vs Statistics:
- Parameters describe population characteristics
- Statistics describe sample characteristics
- Statistics are used to estimate unknown population parameters
- Important for making data-driven decisions